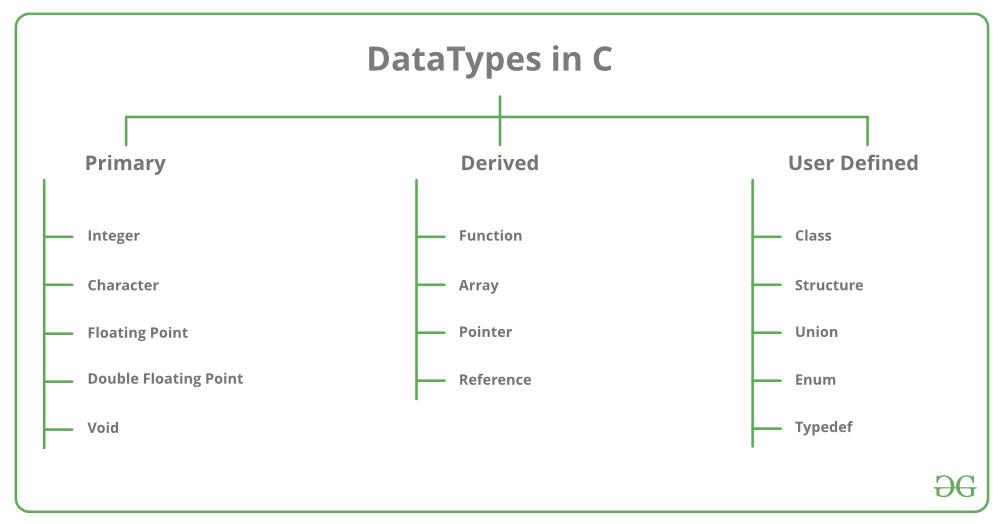
Welcome to the "What about C" repository!
This repository serves as a comprehensive resource for learning and practicing C programming. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced programmer, you'll find valuable content here to enhance your understanding and skills in C programming.
The primary goal of this repository is to provide a structured approach to learning C programming through code breakdowns, projects, and problem-solving exercises. By exploring the content offered here, you'll gain a solid foundation in C programming and develop the confidence to tackle more complex challenges.
Certainly! Here's the complete text with all the sections included in one message:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, world!\n");
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("This is output in C.\n");
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
// This is a single-line comment
/* This is a
multi-line comment */
printf("Hello, world!\n");
return 0;
}

#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int age = 25;
float weight = 65.5;
char gender = 'M';
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int integerVariable = 10;
float floatVariable = 3.14;
char charVariable = 'A';
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#define PI 3.14
int main() {
const int MAX_VALUE = 100;
printf("PI: %f\n", PI);
printf("Max Value: %d\n", MAX_VALUE);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 10, b = 5;
printf("Addition: %d\n", a + b);
printf("Subtraction: %d\n", a - b);
printf("Multiplication: %d\n", a * b);
printf("Division: %d\n", a / b);
printf("Modulus: %d\n", a % b);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main() {
bool isTrue = true;
bool isFalse = false;
printf("isTrue: %d\n", isTrue);
printf("isFalse: %d\n", isFalse);
return 0;
}
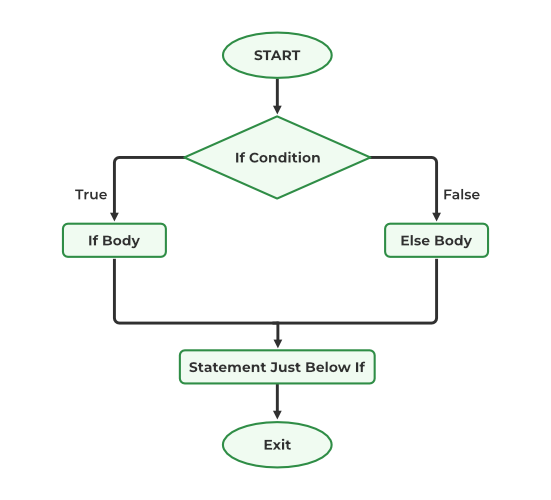
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num = 10;
if (num > 0) {
printf("Positive number\n");
} else {
printf("Negative number\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int day = 3;
switch(day) {
case 1:
printf("Monday\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("Tuesday\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("Wednesday\n");
break;
default:
printf("Invalid day\n");
}
return 0;
}
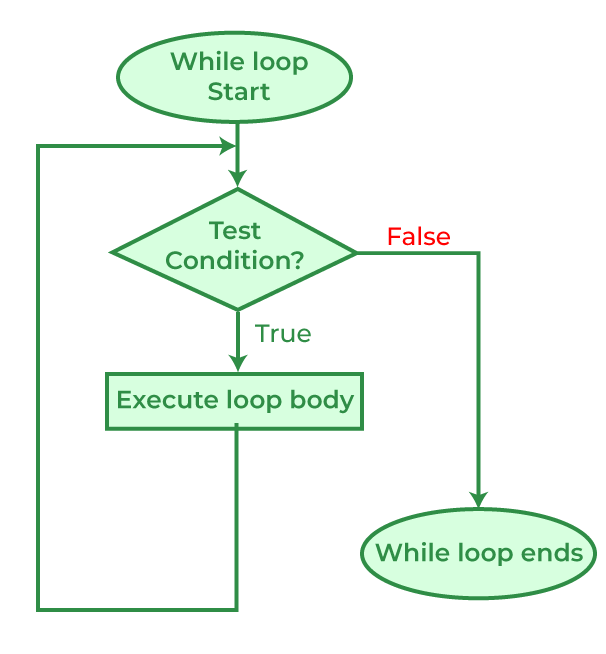
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i = 0;
while (i < 5) {
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", i);
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i == 5) {
break; // Exit the loop
}
if (i % 2 == 0) {
continue; // Skip even numbers
}
printf("%d ", i);
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int arr[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char str[] = "Hello, world!";
printf("%s\n", str);
printf("Length: %d\n", strlen(str));
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num;
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
printf("You entered: %d\n", num);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num = 10;
printf("Value: %d\n", num);
printf("Memory Address: %p\n", &num);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num = 10;
int *ptr = #
printf("Value: %d\n", *ptr);
printf("Memory Address: %p\n", ptr);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
int main() {
printf("Sum: %d\n", add(5, 3));
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
void greet(char name[]) {
printf("Hello, %s!\n", name);
}
int main() {
char name[] = "John";
greet(name);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int add(int, int);
int main() {
printf("Sum: %d\n", add(5, 3));
return 0;
}
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int factorial(int n) {
if (n == 0 || n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
}
int main() {
int num = 5;
printf("Factorial of %d: %d\n", num, factorial(num));
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main() {
printf("Square root of 16: %f\n", sqrt(16));
printf("Absolute value of -5: %f\n", fabs(-5));
printf("Power of 2^3: %f\n", pow(2, 3));
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("file.txt", "w");
fprintf(fp, "This is a file.\n");
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("newfile.txt", "w");
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("file.txt", "w");
fprintf(fp, "This is a file.\n");
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp;
char str[50];
fp = fopen("file.txt", "r");
fscanf(fp, "%s", str);
printf("Read String: %s\n", str);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
struct Person {
char name[50];
int age;
};
int main() {
struct Person person1;
strcpy(person1.name, "John");
person1.age = 30;
printf("Name: %s\n", person1.name);
printf("Age: %d\n", person1.age);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
enum Weekday {
Monday,
Tuesday,
Wednesday,
Thursday,
Friday,
Saturday,
Sunday
};
int main() {
enum Weekday today = Tuesday;
printf("Today is %d\n", today);
return 0;
}
Structures allow you to group different data types together under one name. They are useful for organizing data in a meaningful way. Example:
struct Person {
char name[50];
int age;
float salary;
};
Unions are similar to structures but allocate enough memory to hold the largest member. Only one member of the union can be accessed at a time. Example:
union Data {
int i;
float f;
char str[20];
};
File handling in C involves operations like opening, reading, writing, and closing files. Example of writing to a file:
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("file.txt", "w");
fprintf(fp, "Hello, File World!");
fclose(fp);
C provides functions like malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), and free() for dynamic memory allocation. Example:
int *ptr;
ptr = (int *) malloc(5 * sizeof(int));
if (ptr != NULL) {
ptr[0] = 1;
ptr[1] = 2;
// Use ptr
free(ptr);
}
A linked list is a linear data structure where elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. Each element (node) contains data and a pointer to the next node. Example:
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
// Example of creating nodes and linking them
struct Node *head = NULL;
struct Node *second = NULL;
struct Node *third = NULL;
head = malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
second = malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
third = malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
head->data = 1;
head->next = second;
second->data = 2;
second->next = third;
third->data = 3;
third->next = NULL;
Stack follows the Last In First Out (LIFO) principle. Example:
#define MAX 100
int stack[MAX];
int top = -1;
void push(int item) {
if (top >= MAX - 1) {
printf("Stack Overflow");
return;
}
stack[++top] = item;
}
int pop() {
if (top < 0) {
printf("Stack Underflow");
return -1;
}
return stack[top--];
}
Queue follows the First In First Out (FIFO) principle. Example:
#define MAX 100
int queue[MAX];
int front = -1, rear = -1;
void enqueue(int item) {
if (rear == MAX - 1) {
printf("Queue Overflow");
return;
}
if (front == -1) front = 0;
queue[++rear] = item;
}
int dequeue() {
if (front == -1 || front > rear) {
printf("Queue Underflow");
return -1;
}
return queue[front++];
}
Trees are hierarchical data structures with a root node and child nodes. Example:
struct TreeNode {
int data;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
// Example of creating a tree
struct TreeNode *root = NULL;
root = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
root->data = 1;
root->left = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
root->left->data = 2;
root->left->left = NULL;
root->left->right = NULL;
root->right = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
root->right->data = 3;
root->right->left = NULL;
root->right->right = NULL;
Certainly! Here are brief explanations and examples of more searching and sorting algorithms in C:
Bubble Sort repeatedly steps through the list, compares adjacent elements, and swaps them if they are in the wrong order.
void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
Quick Sort is a divide-and-conquer algorithm that selects a pivot element and partitions the array around the pivot.
void swap(int* a, int* b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = (low - 1);
for (int j = low; j <= high - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] < pivot) {
i++;
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
Selection Sort repeatedly finds the minimum element from the unsorted part of the array and swaps it with the first unsorted element.
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n) {
int i, j, min_idx;
for (i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
min_idx = i;
for (j = i+1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
}
int temp = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
Insertion Sort builds the final sorted array one item at a time by inserting each item into its correct position.
void insertionSort(int arr[], int n) {
int i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
Binary Search works on sorted arrays by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half.
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x) {
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
if (arr[mid] < x)
l = mid + 1;
else
r = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
Linear Search sequentially checks each element of the list until a match is found or the whole list has been searched.
int linearSearch(int arr[], int n, int x) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
C supports multithreading via libraries like POSIX threads (pthread). Example of creating threads:
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void *printHello(void *threadid) {
long tid;
tid = (long)threadid;
printf("Hello World! Thread ID, %ld\n", tid);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main () {
pthread_t threads[5];
int rc;
long t;
for (t = 0; t < 5; t++) {
rc = pthread_create(&threads[t], NULL, printHello, (void *)t);
if (rc) {
printf("ERROR; return code from pthread_create() is %d\n", rc);
return -1;
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
Involves managing memory efficiently using techniques like malloc, free, and avoiding memory leaks.
Welcome to the "Problem Solve" section of the repository! Here you'll find solutions to various programming problems.
Feel free to explore the solutions to these problems. Happy coding!
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
Thank you for exploring these C programming examples and explanations! Special thanks to ChatGPT and W3Schools for assisting in this endeavor.